Products--
- Sewage Treatment Plant
- Compact Electrolysis Sewage Treatment Plant
- Effluent Treatment Plant
- Reverse Osmosis Plant
- Filtration
- Ultra Filtration Plant
- Microfiltration
- Nanofiltration Plant
- Demineralisation Plant
- Zero Liquid Discharge Plant
- Softener Plant
- Lamella Clarifier
- Swimming Pool
- Water Harvesting Plants
Services--
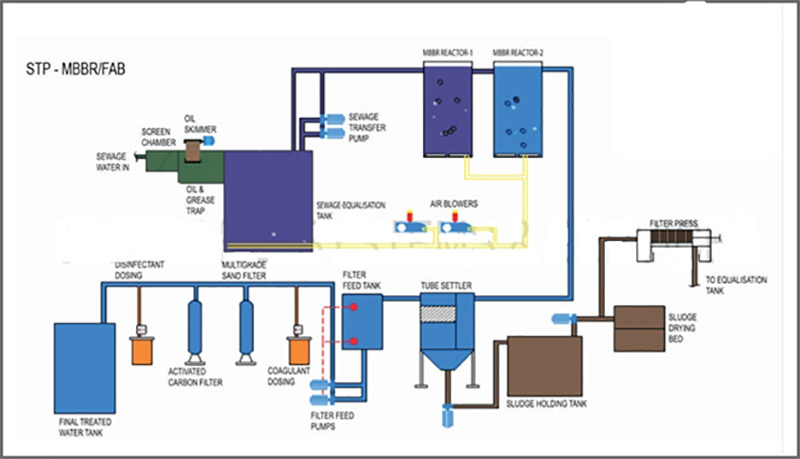
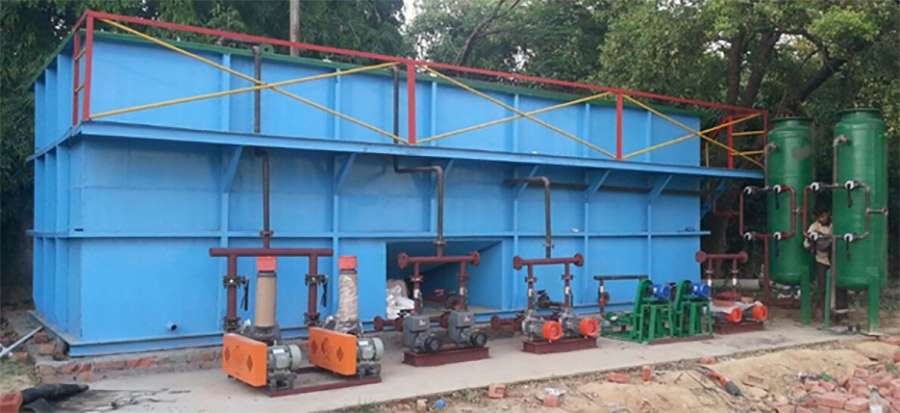
Sewage Treatment Plant
Sewage treatment Plant (STP) is the process of removing contaminants from wastewater, primarily from household sewage. Physical, chemical, and biological processes are used to remove contaminants and produce treated wastewater (or treated effluent) that is safer for the environment. A by-product of sewage treatment is usually a semi-solid waste or slurry, called sewage sludge. The sludge has to undergo further treatment by STP Plant before being suitable for disposal or application to land.
Water from the mains, used by manufacturing, farming, houses (toilets, baths, showers, kitchens, sinks), hospitals, commercial and industrial sites, is reduced in quality as a result of the introduction of contaminating constituents. Organic wastes, suspended solids, bacteria, nitrates, and phosphates are pollutants that must be removed.

Features :
The features of wastewater treatment systems are determined by:
- The nature of the municipal and industrial wastes that are conveyed to them by the sewers.
- The amount of treatment required to keep the quality of the receiving streams and rivers.
Capacity :
- 1 to 1000 m3/day in single.